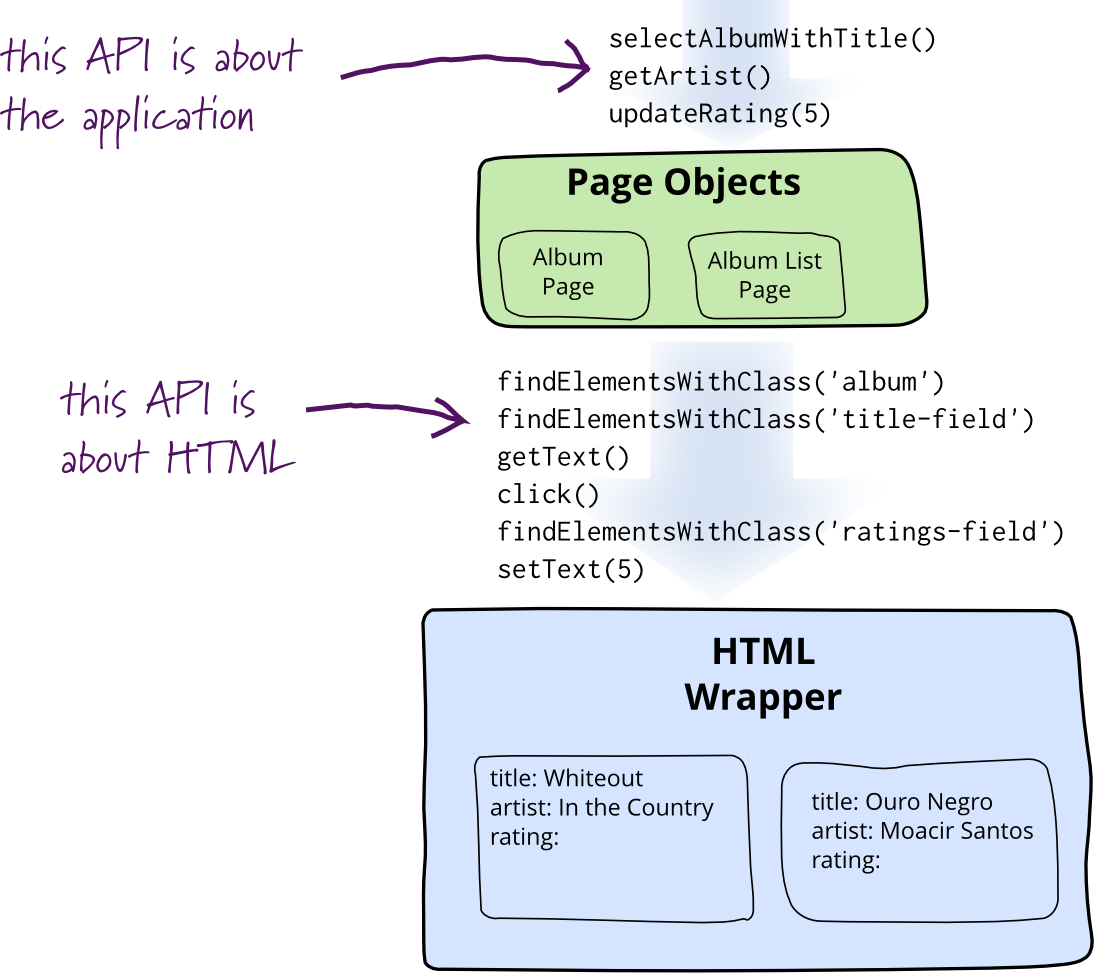
Python-BPF: A New Way to Write eBPF Programs in Python
Python-BPF is a revolutionary open-source library enabling the writing of eBPF programs entirely in Python, compiling them directly into object files. This eliminates the previous cumbersome approach of embedding C code within Python. Leveraging Python's AST and LLVM IR for compilation, Python-BPF supports control flow, hash maps, helper functions, and more, significantly streamlining eBPF development and offering a new production-ready option.