East Asian Emissions Reductions and their Impact on Global Warming: RAMIP Simulation Results
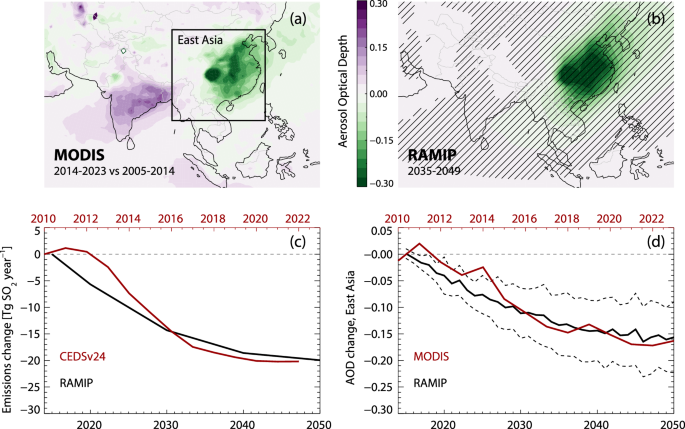
A new study uses RAMIP simulations to quantify the impact of recent East Asian air pollution emission reductions on climate change. The study finds that a 20 Tg/year reduction in East Asian SO2 emissions led to a 0.07 ± 0.05 °C increase in global mean surface temperature and significant warming in the North Pacific. Simulation results match MODIS observations of aerosol optical depth changes, suggesting that RAMIP effectively captures the impact of real-world reductions. The study also notes that other factors, such as increased methane concentrations and shipping emission reductions, likely contributed to global warming, but East Asian emission reductions played a significant role in the accelerated rate of global warming over the past decade.