OpenAI Unleashes gpt-oss: Powerful, Locally-Runnable Open-Weight LLMs
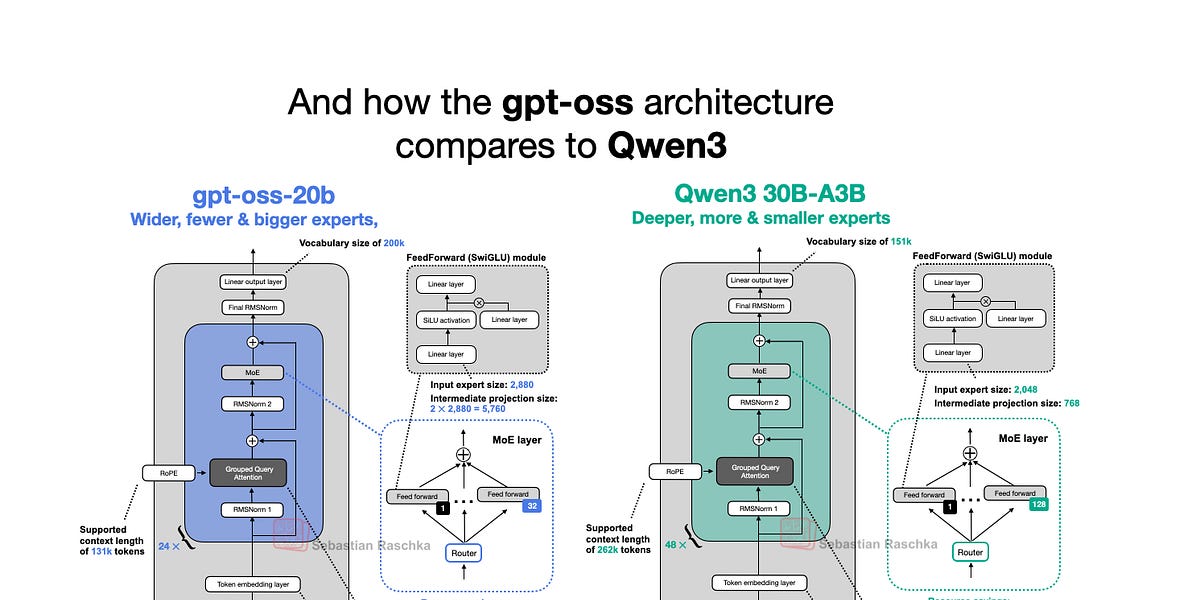
OpenAI this week released gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b, their first open-weight models since GPT-2 in 2019. Surprisingly, thanks to clever optimizations, they can run locally. This article delves into the gpt-oss model architecture, comparing it to models like GPT-2 and Qwen3. It highlights unique architectural choices such as Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), Grouped Query Attention (GQA), and sliding window attention. While benchmarks show gpt-oss performing on par with closed-source models in some areas, its local runnability and open-source nature make it a valuable asset for research and applications.
Read more
