Page Objects: Making Your UI Tests Less Brittle
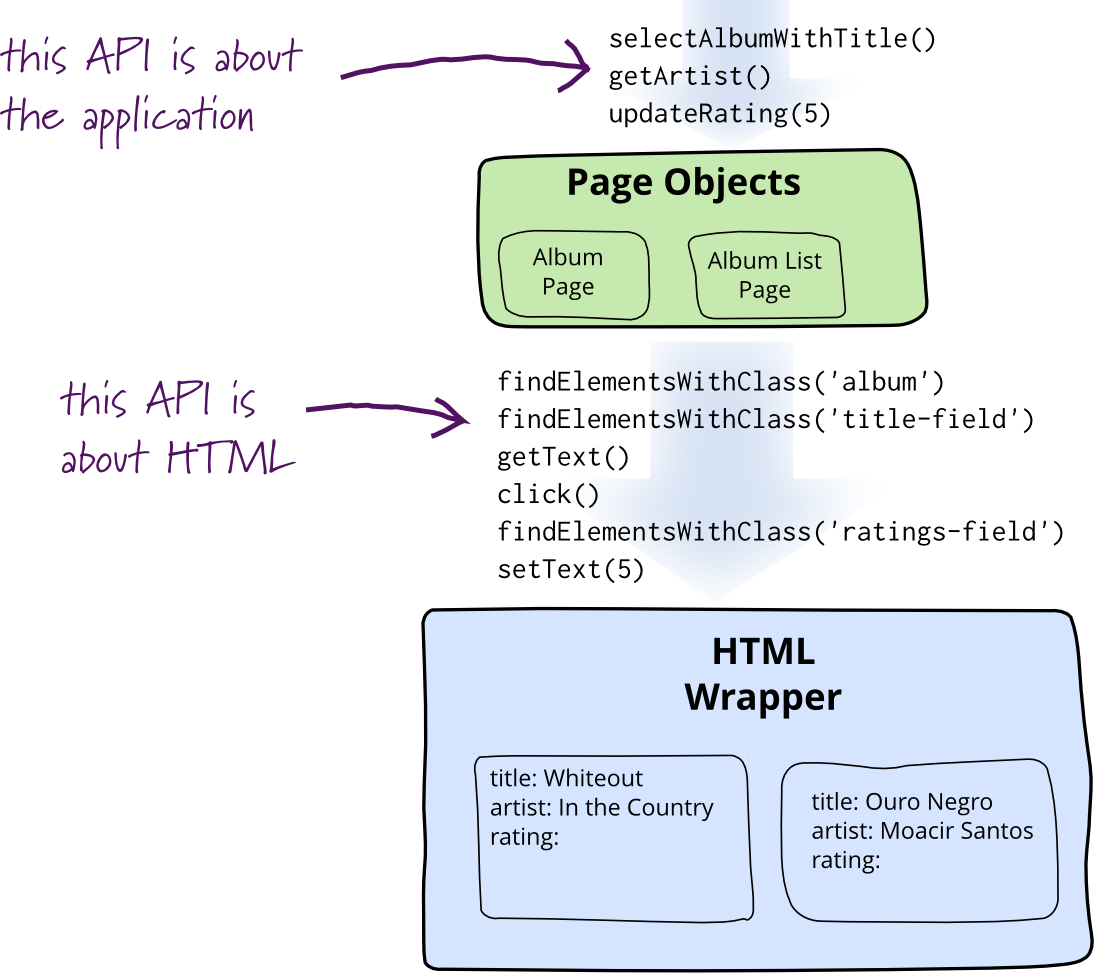
Testing web pages requires interacting with elements, but directly manipulating HTML makes tests fragile. Page Objects solve this by encapsulating a page or fragment as an application-specific API. This allows interacting with elements without directly accessing HTML. The goal is to mimic user actions, providing a clean interface that hides underlying widgets. Text fields use string accessors, checkboxes booleans, and buttons action-oriented methods. Good Page Objects model the user's perspective, not the UI's internal structure, returning basic data types or other Page Objects. There's debate on including assertions within Page Objects. The author prefers keeping assertions in test scripts, avoiding bloated Page Objects and using assertion libraries to reduce redundancy. This pattern works across various UI technologies, useful not just for testing but also as a scripting interface for applications.
Read more