Bauble: A Functional Approach to 3D Art with Signed Distance Functions
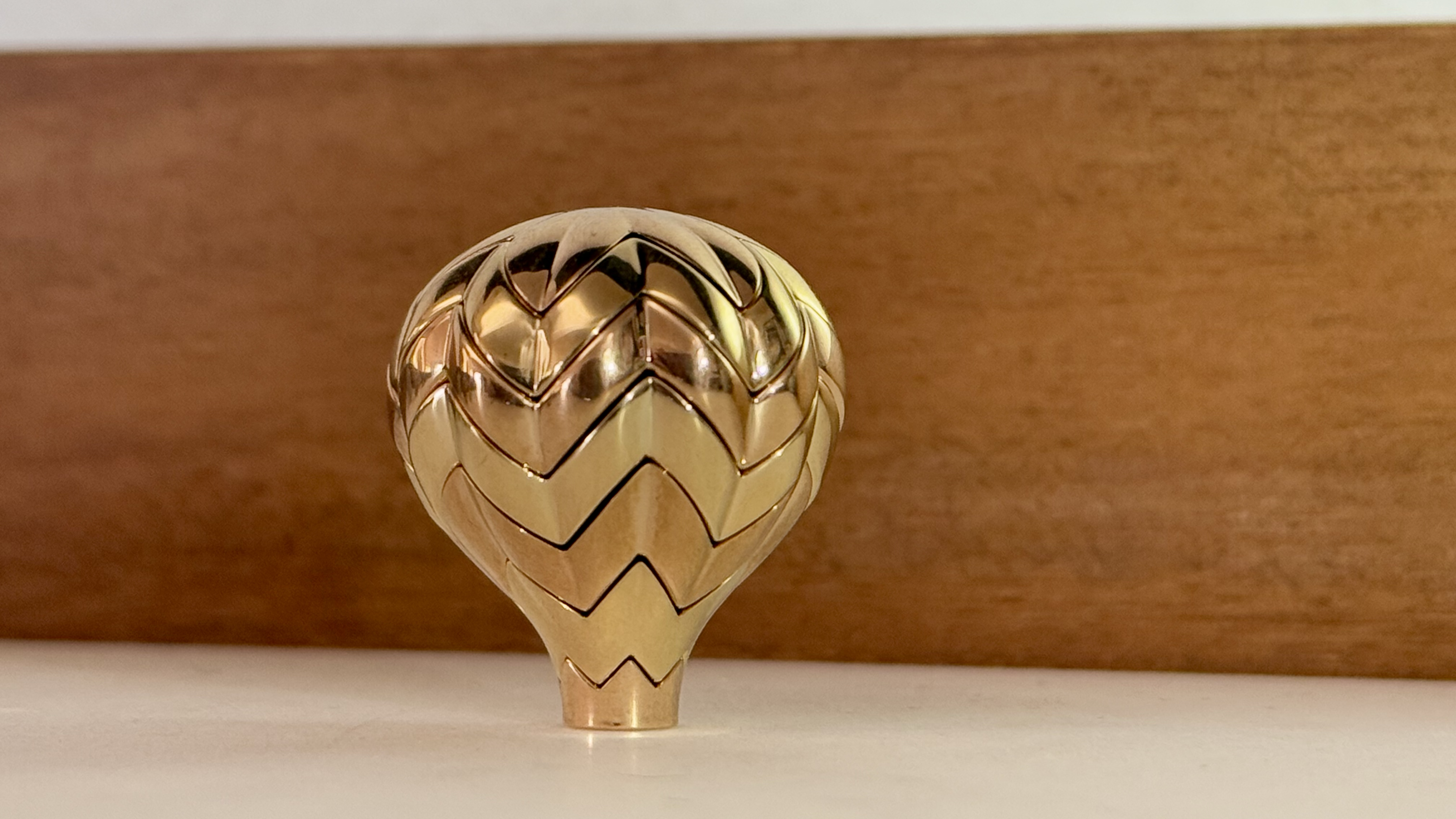

Ian Henry recounts his journey building Bauble, a tool for creating interactive 3D graphics using signed distance functions (SDFs) and the Janet programming language. Initially a simple GLSL string concatenator, Bauble evolved to include features like animation, custom dynamic expressions, and lighting. However, its complexity led to a complete rewrite, resulting in a robust compiler and comprehensive documentation. Now, Bauble empowers users to create stunning 3D art with relative ease.