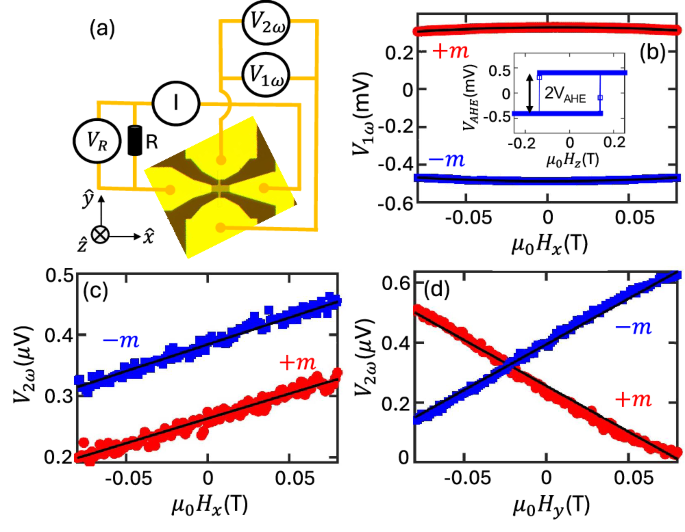
Apple's C1 Modem: Lower Power Consumption, Comparable Performance

Apple's self-developed C1 modem, debuting in the iPhone 16e, shows comparable performance to previous 5G chips but with significantly reduced power consumption. Tests in lab and real-world scenarios (like subway trains) show the C1 matching Qualcomm's modems in 5G speeds, while boasting roughly a 24% lower average power consumption. The iPhone 16e achieved 53 minutes more 5G video streaming time than the iPhone 16. While the iPhone 16e has a larger battery, the results highlight the significant power efficiency gains of Apple's in-house silicon design, going beyond just saving licensing fees. The success suggests Apple's reported development of a C2 modem is likely.