ChatGPT-powered Da Vinci Robot Performs Autonomous Gallbladder Removal
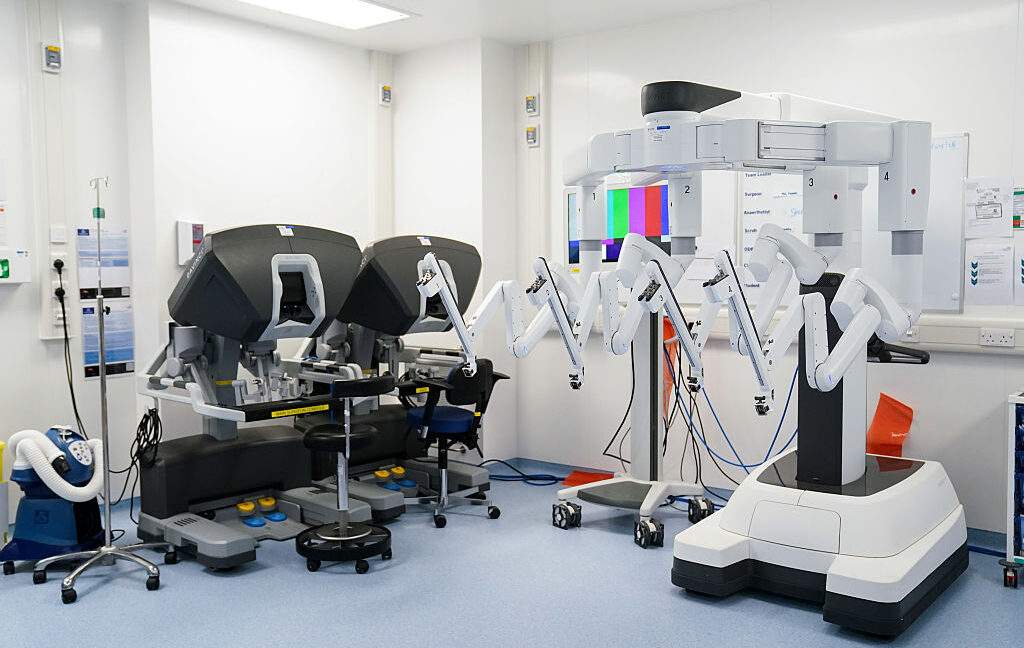
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University integrated a ChatGPT-like AI with a Da Vinci surgical robot, achieving autonomous gallbladder removal. Unlike previous robot-assisted surgeries relying on pre-programmed actions, this system, SRT-H, uses two transformer models for high-level task planning and low-level execution. The high-level module plans and manages the procedure, while the low-level module translates instructions into precise robotic arm movements. Built upon the widely adopted Da Vinci platform, SRT-H demonstrates greater flexibility and adaptability, marking a significant leap forward in AI-assisted surgery.