Sub-Pixel Motion Detection with Ferroelectric Polymer-Based Memristor
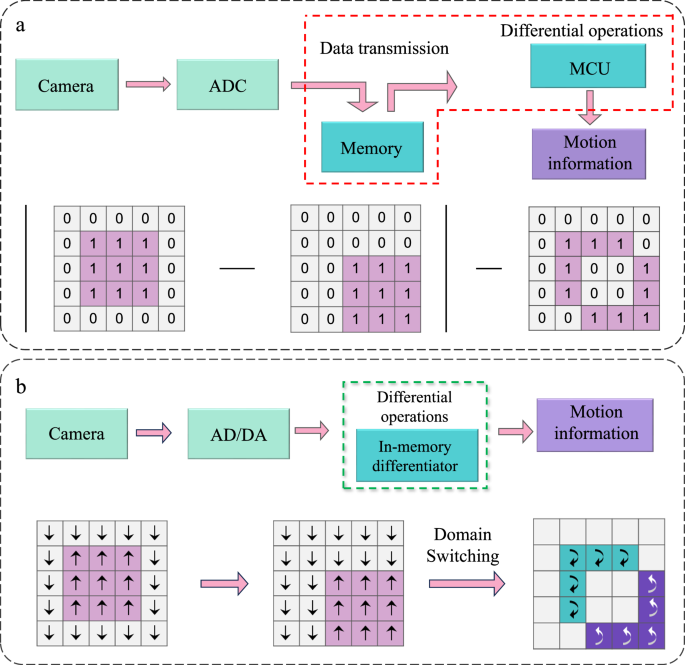
Researchers have developed a novel ferroelectric random-access memory (FeRAM) using solution-processed ferroelectric P(VDF-TrFE) thin films for sub-pixel motion detection. This FeRAM, based on a passive crossbar array of capacitors, leverages the nonlinear dynamics of ferroelectric domains to effectively eliminate sneak-path issues. By switching ferroelectric domains via controlled electric field polarity, the system stores and processes image information, directly extracting image differences. This enables applications like calculating derivatives of mathematical functions and identifying moving objects. The system boasts high accuracy, low power consumption, and eliminates the need for additional memory units, showing significant potential for applications in video surveillance and defect detection.