Six Design Patterns to Secure LLM Agents Against Prompt Injection
2025-06-13
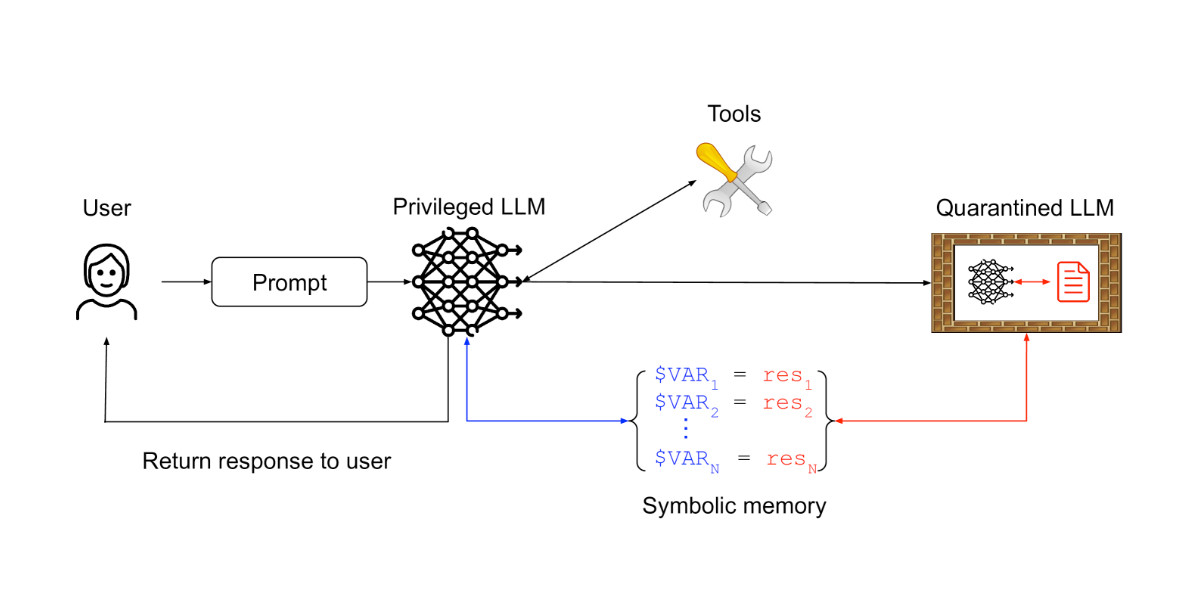
A new paper from researchers at IBM, Invariant Labs, and other institutions introduces six design patterns to mitigate the risk of prompt injection attacks against large language model (LLM) agents. These patterns constrain agent actions, preventing arbitrary task execution. Examples include the Action-Selector pattern, which prevents tool feedback from influencing the agent; the Plan-Then-Execute pattern, which pre-plans tool calls; and the Dual LLM pattern, which uses a privileged LLM to coordinate an isolated LLM, avoiding exposure to untrusted content. The paper also features ten case studies across various applications, offering practical guidance for building secure and reliable LLM agents.