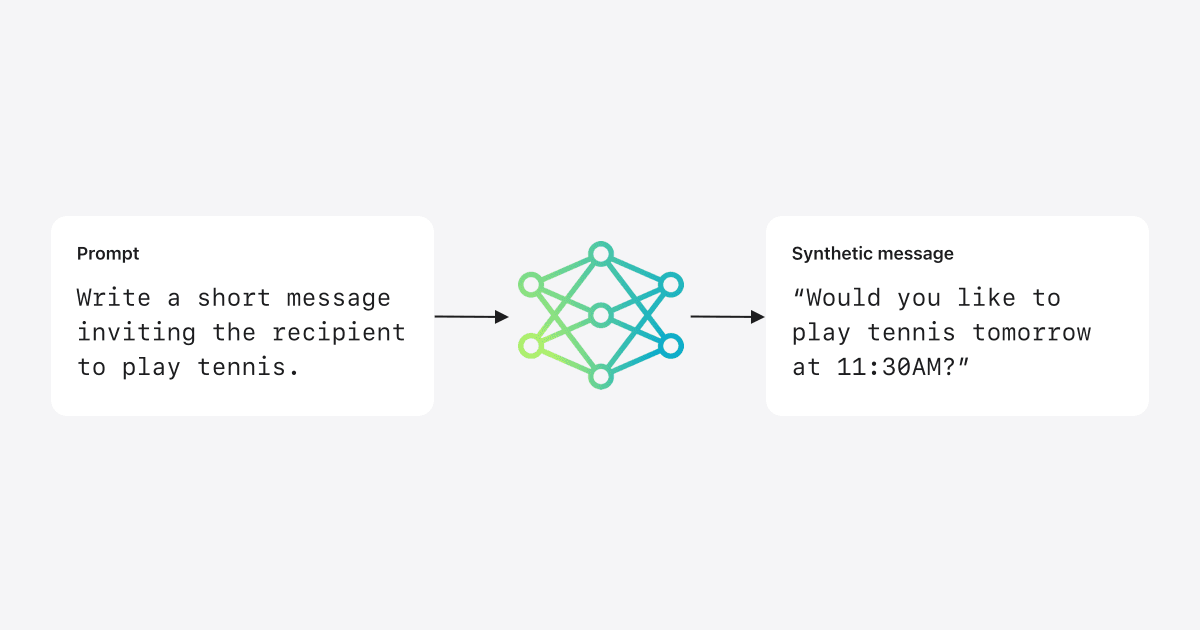
Will AI Code Generation Replace Human Engineers?

This article explores the productivity comparison between AI code generation models (like Gemini) and human engineers. While currently a single engineer might be more efficient, AI model costs are decreasing, and their capabilities are improving. In the future, a large number of AI models working together, coupled with codebases and development tools optimized for AI, will far surpass human teams in efficiency. The article predicts that the software engineering industry will move towards industrialization, and the role of engineers will shift to managing and supervising AI as 'factory supervisors'.