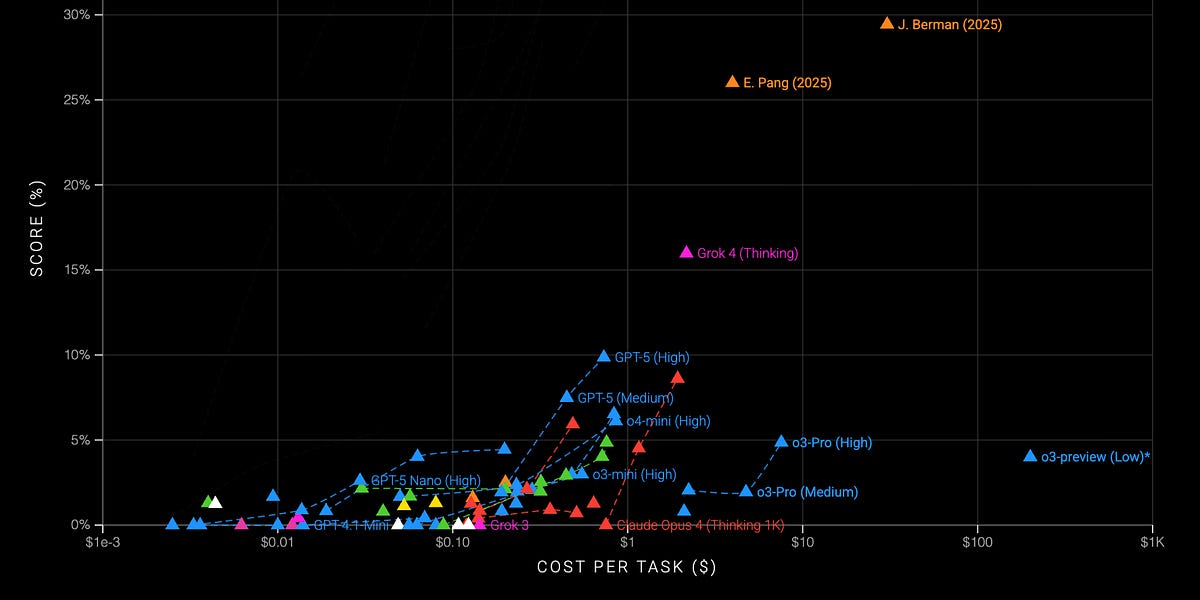
Anthropic Fixes Three Infrastructure Bugs Affecting Claude

Anthropic acknowledged that between August and early September, three infrastructure bugs intermittently degraded Claude's response quality. These bugs, causing misrouted requests, output corruption, and compilation errors, impacted a subset of users. Anthropic detailed the causes, diagnosis, and resolution of these bugs, committing to improved evaluation and debugging tools to prevent recurrence. The incident highlights the complexity and challenges of large language model infrastructure.